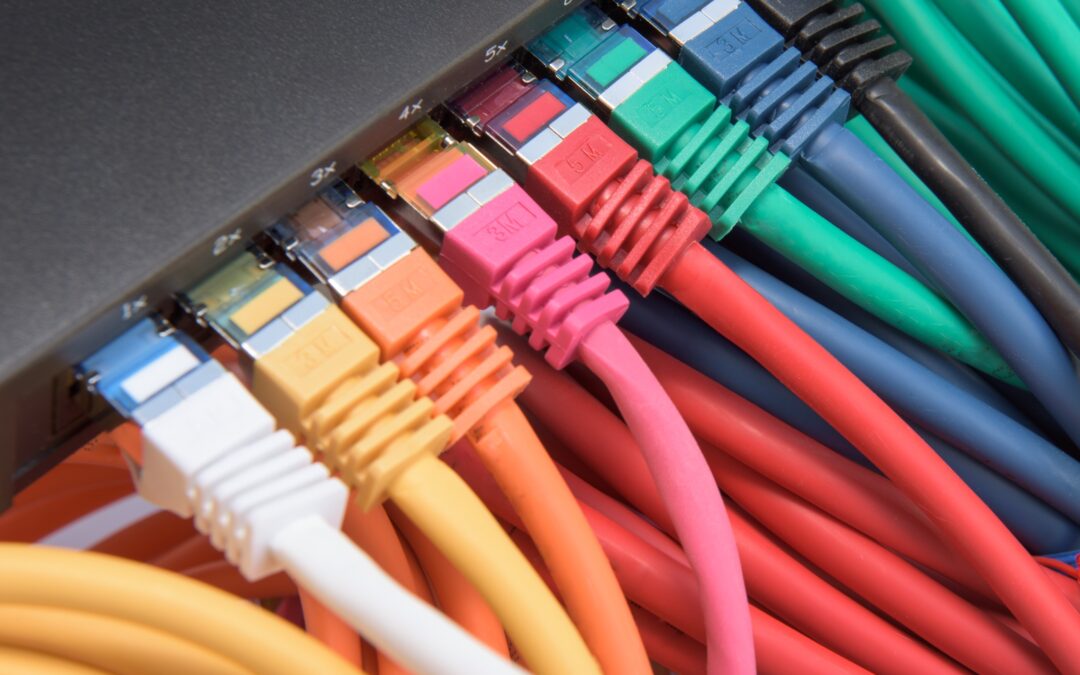
The transfer of digital data wouldn’t be possible without cables. Two main types of cables that are leading the way in enabling VoIP systems and connecting servers or terminal equipment such as switches, routers, workstations, and printers are the newest model of copper cables, Cat6 cables, and fiber optic cables. Read on to explore the differences between Cat6 cables and fiber optic cables to make an informed decision for your business needs.
How Cat6 Cables and Fiber Optic Cables Work
At Data Safe, we install both types of cables.
Understanding Cat6 Cables
Cat6, or Category 6, refers to a standardized cable used in Ethernet networks. It belongs to the family of twisted pair cables, which are composed of copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference.
Construction of Cat6 Cables
Cat6 cables typically consist of four twisted pairs of copper wires enclosed in a plastic sheath. The twisting of pairs helps mitigate the effects of crosstalk, ensuring a more stable and reliable data transmission.
Enhanced Performance of Cat6 Cables
One of the key distinguishing features of Cat6 cables is their improved performance compared to their predecessors, such as Cat5 and Cat5e. Cat6 cables support higher data transfer rates and have greater bandwidth, making them suitable for applications demanding faster and more robust connectivity.
Understanding Fiber Optic Cables
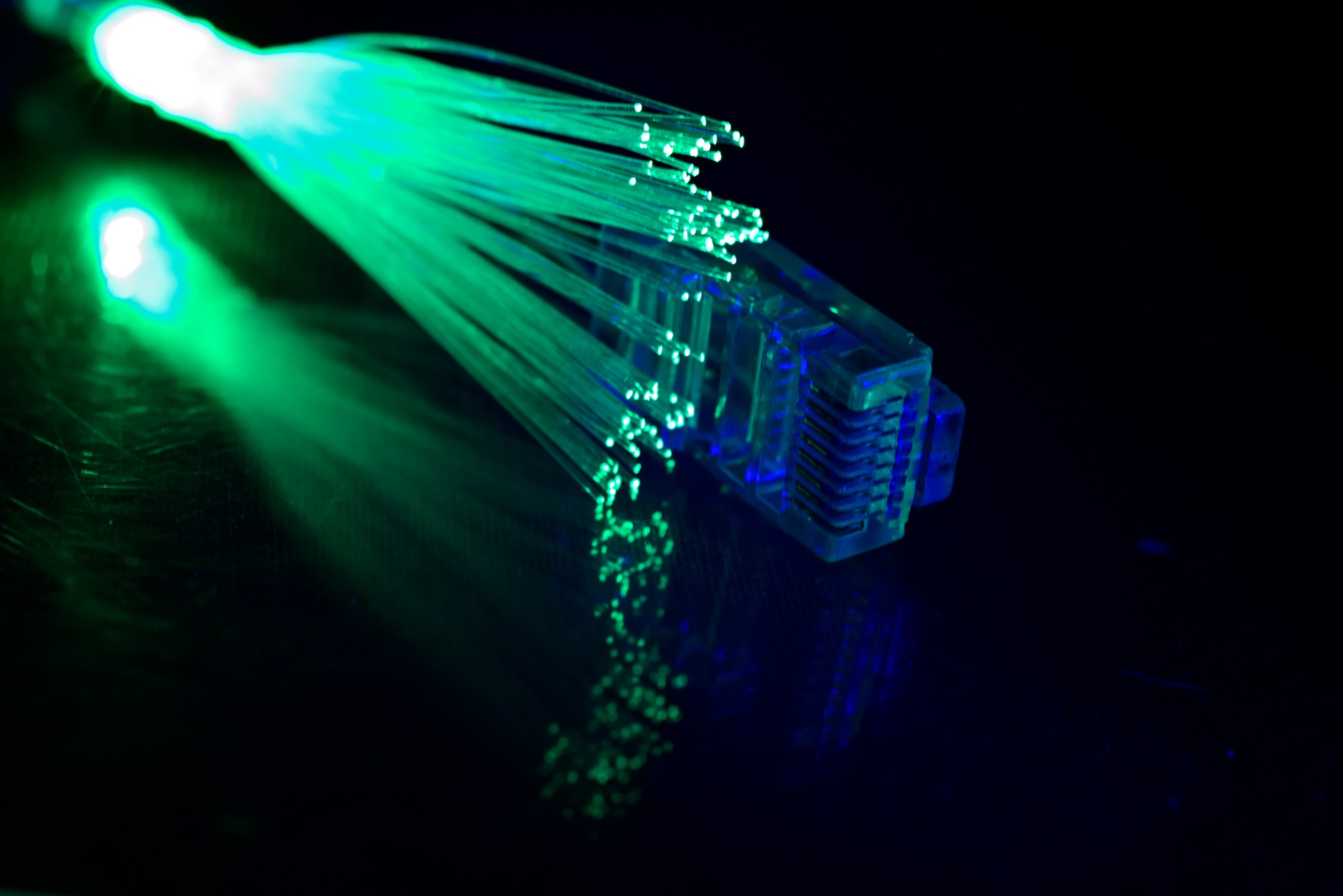
Core Components of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are made of glass or plastic fibers, each thinner than a human hair. These fibers carry pulses of light, serving as the medium for transmitting data. There is one more layer of glass that is wrapped around the central fiber to enhance the quality of signal transmission.
Light-Based Communication
Unlike traditional copper cables that transmit electrical signals, fiber optic cables utilize the principles of total internal reflection. This involves bouncing light signals off the inner walls of the fiber core, ensuring minimal signal loss over long distances.
Types of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables come in two main types: single-mode and multi-mode.
Single-Mode Fiber Optic Cables
Single-mode fiber optic cables are designed to carry a single mode or ray of light. This focused approach gives single-mode fibers distinct advantages in long-distance communication and applications requiring high bandwidth and minimal signal dispersion.
The core of a single-mode fiber optic cable is typically around 8 to 10 micrometers in diameter. Single-mode fibers typically use a laser diode as the light source. The laser produces a coherent and narrow beam of light, ensuring precise and efficient data transmission. Dispersion refers to the spreading of light pulses as they travel through the fiber. Single-mode fibers exhibit low dispersion, meaning that light pulses remain well-defined and do not spread out over long distances.
Single-mode fiber optic cables are commonly used in long-distance telecommunications networks, including undersea cables that connect continents. They are also prevalent in enterprise networks, data centers, and applications requiring high-speed internet connections.
Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Cables
Multi-mode fiber optic cables carry multiple rays of light simultaneously. Unlike single-mode fibers that transmit a single focused beam of light, multi-mode fibers have a larger core size, allowing for the transmission of multiple light paths. This characteristic makes them suitable for shorter-distance communication and applications where high bandwidth is crucial but where the increased dispersion of light is acceptable.
The core of a multi-mode fiber optic cable is larger than that of a single-mode cable, typically ranging from 50 to 62.5 micrometers in diameter. The increased core size enables the transmission of multiple light modes.
Multi-mode fibers often use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) as light sources. These sources emit a broader range of light, which aligns with the larger core size of multi-mode fibers.
Multi-mode fibers are suitable for shorter-distance communication, typically within the range of a few kilometers. They are well-suited for applications within buildings, campuses, and local area networks (LANs).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cat6 and Fiber Optic Cables
Cat6 Cables
Advantages
Cost-Effective: Cat6 cables are generally more budget-friendly than fiber optic cables.
Easy Installation: Cat6 cables are easier to install and terminate, making them a preferred choice for smaller setups.
Suitable for Short to Medium Distances: Ideal for networking within a building or a campus.
Disadvantages
Limited Bandwidth: Cat6 cables have a lower bandwidth compared to fiber optic cables.
Susceptible to Interference: They can be affected by electromagnetic interference, potentially impacting data transfer.
Fiber Optic Cables
Advantages:
High Bandwidth: Fiber optic cables offer significantly higher bandwidth, allowing for faster data transfer.
Immune to Electromagnetic Interference: The use of light signals makes fiber optic cables impervious to electromagnetic interference.
Long Distances: Suitable for long-distance communication without signal degradation.
Disadvantages
Cost: Fiber optic cables can be more expensive to install.
Installation Complexity: Installation and termination of fiber optic cables require specialized skills and tools.
Choosing the Best Cable for Your Business
When choosing between Cat6 and fiber optic cables, you should keep the following considerations in mind:
Budget: If cost is your primary concern and the communication distance is short, Cat6 may be a more practical choice.
Speed and Bandwidth: If your business requires high-speed data transfer over longer distances and larger bandwidth, you may want to opt for fiber optic cables.
Maintenance Requirements
Regardless of the cable type you choose, regular maintenance is important for optimal performance. You can rely on our experts to inspect your company’s cables for wear and tear, ensure proper connections, and monitor for any signs of interference. Regular checks can prevent downtime and ensure a reliable network.
When it comes to handling cables, remember that it is important to minimize end-face contamination by cleaning the end faces of cables before mating. Also, make sure to avoid excessive bending as it can negatively affect the quality of data transmission.
If you need to power your business with cables, Data Safe Group LLC is here to help. We can advise whether Cat6 or fiber optic cables are a better option for your company. Contact us today for a consultation.

